Troubleshooting
Common error messages
Cannot connect to the Docker daemon
The Docker daemon is required for running any docker container. If you get the following error:
docker: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?.
See ‘docker run –help’.Command Line/Terminal:
try starting the Docker daemon with the dockerd command:
sudo dockerdor with your service manager:
systemctl start docker # for systemd, or
sudo service docker start # for open-rcDocker Desktop app:
The Docker daemon should automatically start when you open the desktop application. Check if docker is running in the background. If it is not, then open the Docker desktop application.
Error 403 on the dashboard
You are not authorized. Your browser has cached the dashboard pages, however you may have restarted the frontend or backend processes and lost the authorized session.
To fix this error, try to log in again. See login credentials at the Project setup page for more information.
Port 5000 is already in use
The backend is hard-coded to use port 5000 and will not start if the port is already in use. Try to kill the process that is currently using port 5000 before re-running.
Linux/MacOS:
You can find the process using the port with lsof -i :5000, which will give a pid.
Kill the process with kill -9 <pid>.
On MacOS, this process could be an AirPlay server that respawns immediately after getting killed. To disable it, uncheck “AirPlay Receiver” in System Preferences → Sharing.
Windows: First find the process (pid) that is using port 5000. Open powershell and enter the following command:
netstat -ano | findstr :5000This should give you a list of processes that are currently using port 5000 along with their PID.
Using the PID you found previously, enter the following command after replacing “TYPEYOURPIDHERE” with the PID of the process you want to kill:
taskkill /PID TYPEYOURPIDHERE /FECONNREFUSED when starting backend or GraphDB exceptions with no GraphDB messages
There might be a conflict with the definition of localhost in IPv4 and IPv6.
Replace localhost with 127.0.0.1 in backend/config/index.js,
for the graphdb field:
const config = {
graphdb: {
addr: isProduction ? 'http://127.0.0.1:7200' : `http://${isDocker ? 'host.docker.internal' : '127.0.0.1'}:7200`,
},
...Module not found
This usually occurs due to outdated dependencies. This issue can can be resolved by re-running yarn install.
Inconsistent data across pages
Example cases:
- Deleted data entries still show up somewhere.
- Dropdown menus don’t list all entries.
This is a bug. To work around it, clear both the GraphDB and MongoDB databases.
- GraphDB: Go to http://localhost:7200 in your browser and click the button pictured below:
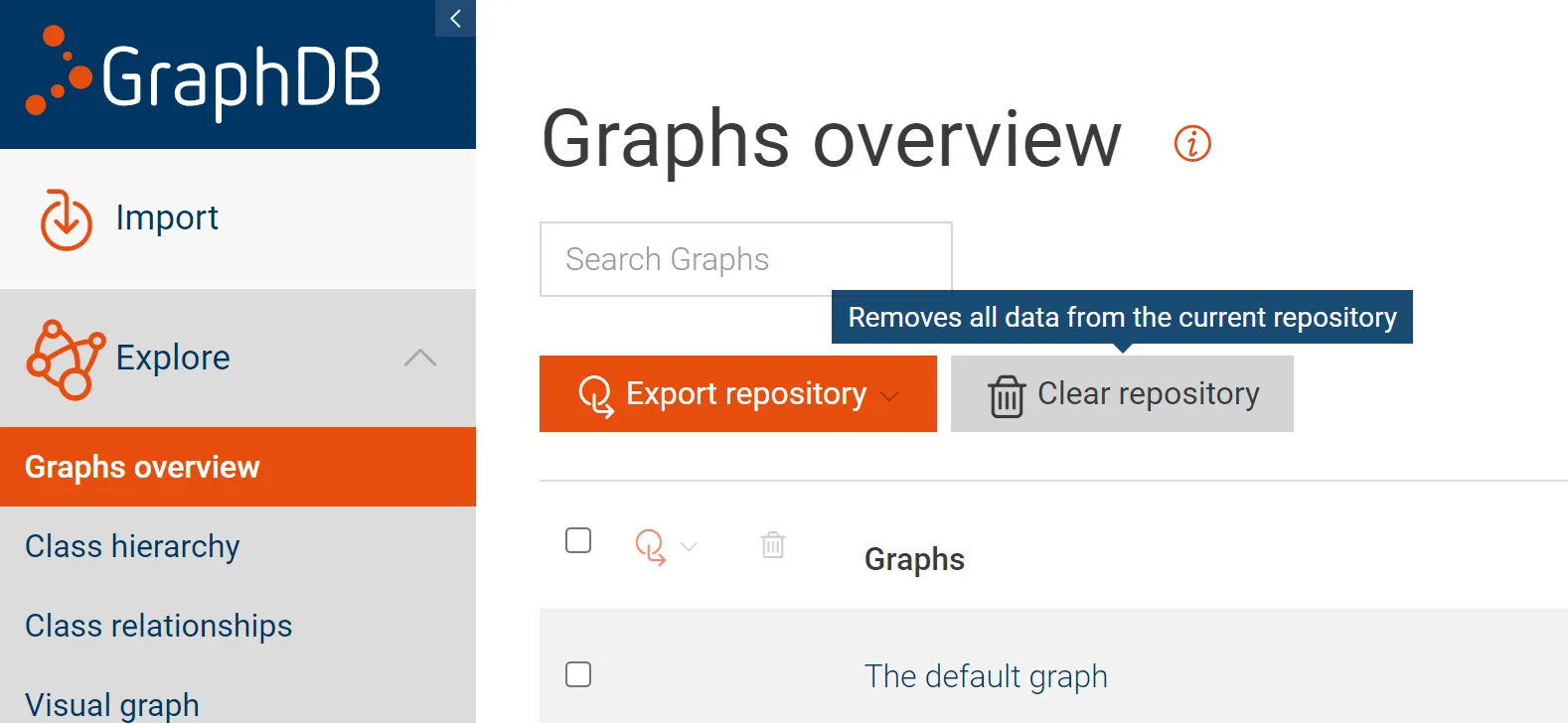
- MongoDB: One way to clear the MongoDB databse is to re-create the entire Docker container:
Linux/MacOS:
docker remove mongo
docker run --name mongo -p 27017:27017 --restart unless-stopped -d mongo:latestwhere mongo (not mongo:latest) are replaced with the name of your docker container.
Windows: Open a new Powershell window and enter the following commands:
docker rm mongo
docker run --name mongo -p 27017:27017 --restart unless-stopped -d mongo:latestNote: if you used a different name for the MongoDB container than the one in the project setup documentation, replace all instances of “mongo” with the name of your container.
Tips and tricks
- Open the console in your browser to see the error messages
- On most browsers, right-click on the page to open the options menu. Click
Inspectto open the Developer Tools window. On the top of the window, click onconsoleto view the error messages.
- On most browsers, right-click on the page to open the options menu. Click
- Ask for help if you get stuck
Finding out which frontend component triggers which API/query
Open the web client and the terminal window where you ran yarn start in backend/ side-by-side.
Interact with the frontend and observe the logs printed on the terminal.
If the API calls a SPARQL query, it will also log the exact query.